LAND SURVEY TERMS
GLOSSARY OF U.S. BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT SURVEYING AND MAPPING TERMS G
Land Survey Terms, A convenient source for our clients and website visitors
G
G&M – Geography and Map; geography and Map Div.
GA – Georgia; Geographic access; Geographical Association
GAC – Geological Assn. of Canada; Global Area Composite; Geospatial Advisory Committee (USFS)
GAMS – GIS azimuth measuring system
GAP – Any space where aerial photographs fail to meet minimum coverage requirements; Gap Analysis Program (USNBS); Geographic Application Program; Google Ancient Places
GAT (Greenwich Apparent Time) – Local apparent time at the Greenwich meridian; the arc of the celestial equator, or the angle at the celestial pole between the lower branch of the Greenwich celestial meridian and the hour circle of the apparent or true sun, measured westward from the lower branch of the Greenwich celestial meridian through 24 hours, Greenwich hour angle of the apparent or true sun, expressed in time units, plus 12 hours.
<span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: 18px;”><span style=”color: #004fbd;”><img class=”alignleft wp-image-9816″ src=”https://haller-blanchard.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/the-safe-companies-contact-us.gif” alt=”” width=”38″ height=”38″ />Please feel free to</span> <a href=”https://haller-blanchard.com/contact-land-survey-company//”>contact us</a> <span style=”color: #004fbd;”>about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. </span></span><span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: 18px;”><span style=”color: #004fbd;”>We are here now and ready to answer.</span>
</span>
GCT (Greenwich Civil Time) – In modern usage, civil time refers to statutory time scales designated by civilian authorities or to local time indicated by clocks.
GD (Land Status Records) – Gold.
GEO (Land Status Records) – Geothermal.
GEOL STR (Land Status Records) – Geologic structure.
GHA (Greenwich Hour Angle) – Greenwich Hour Angle, abbreviated GHA, is the angular measure of the celestial body from the Greenwich Meridian (also known as the Prime Meridian) along the celestial equator.
GLO (Land Status Records) – General Land Office.
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) – The mean solar time at the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight.
GR DIST (Land Status Records) – Grazing District.
GR LIC (Land Status Records) – Grazing license.
GR LSE (Land Status Records) – Grazing lease.
GR PER (Land Status Records) – Grazing permit.
GSR MER (Land Status Records) – Gila and Salt River Meridian
GENERALIZATION – Modification of contours on a source map preparatory to reduction and conversion to larger contour interval to show terrain without clutter.
GENERAL LAND OFFICE – The agency which was formerly responsible for the execution of the public-land laws relating to cadastral surveys, land disposals, and to various other activities with respect to the administration and management of the public lands.
GENERAL PURPOSE MAP (USGS) – A map designed to provide a large amount of general information for widespread public use.
GEODESIC – The shortest line connecting two given points on the surface of an ellipsoid.
GEODESY – The science which treats mathematically the shape and size of the earth; also, the branch of surveying in which measurements are made for determining the shape of the earth including precise horizontal and vertical positions on its surface. One branch of geodesy includes gravity forces.
GEODETIC – Referred to or based on considerations of geodesy.
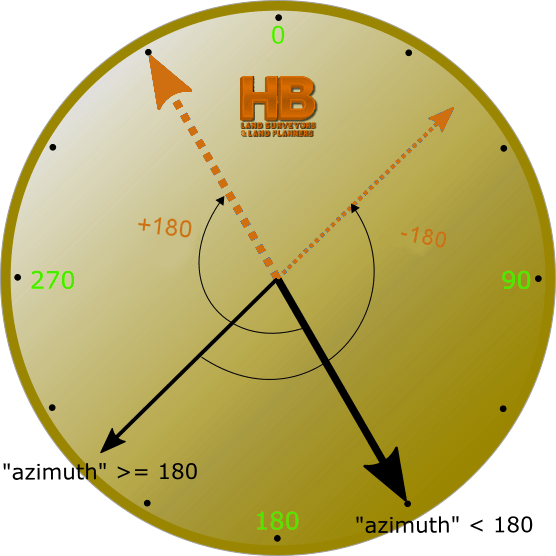
GEODETIC AZIMUTH – The horizontal angle at station A measured from a north-south plane (perpendicular to the reference ellipsoid) clockwise to an ellipsoidal normal section passing through station B. Geodetic azimuth is determined by applying a correction to astronomic azimuth or by computations on the referenced ellipsoid. The
azimuth from A toward B is the forward azimuth while the azimuth from B toward A is the back azimuth of station B. See GEODETIC.
![]() Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Phone
GEODETIC CONTROL – A system of horizontal or vertical survey stations that have been established and adjusted by geodetic methods.
GEODETIC CONTROL DIAGRAMS – A series of index maps which show the location of precise surveys of U.S.C. & G.S., U.S.G.S. and other agencies.
GEODETIC COORDINATES – Quantities which define a horizontal position on an ellipsoid of reference with respect to a geodetic datum. See GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES.
GEODETIC LATITUDE – 1) the angle between the plane of the equator of the referenced ellipsoid and the normal to the ellipsoid surface.
2) The latitude of a point determined by geodetic methods.
GEODETIC LEVELING – Spirit leveling of a high order of accuracy, generally extended over large areas, with application of orthometric corrections, to furnish accurate vertical control for surveying and mapping operations.
GEODETIC LINE – See GEODESIC.
GEODETIC LONGITUDE – 1) The dihedral angle between an arbitrary meridian and the meridian of an ellipsoidal normal.
2) A longitude determined by geodetic methods.
GEODETIC NORTH – The direction of the pole of the earth ellipsoid of reference.
GEODETIC POSITION – Geographic coordinates of a point determined by geodetic methods.
GEODETIC SATELLITE – An earth orbiting satellite equipped to make it useful for geodetic observations.
GEODETIC SURVEY – A precise survey of considerable extent which takes into account the shape of the earth.
GEODIMETER – Trade name for an electronic distance measuring system.
GEOGRAPHIC – Signifying basic relationship to the earth considered as a globe-shaped body. The term “geographic” is applied alike to data based on the ellipsoid (geodetically determined) and on the geoid (astronomically determined).
GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATES – (U.S.C. & G.S. Sp. Pub 242) An inclusive term, used to designate both geodetic coordinates and astronomic coordinates.
GEOGRAPHIC POSITION – Coordinates usually expressed as latitude and longitude of a point which are usually determined by geodetic methods but occasionally by astronomic observations.
GEOID – The figure of the earth considered as a sea level surface extended continuously through the continents. It is a theoretically continuous surface that is perpendicular at every point to the direction of gravity (the plumb line). It is the surface of reference for astronomic observations and for geodetic leveling.
GEOLOGIC SURVEY – A survey or investigation of the character and structure of the earth.
GEOLOGY MAP – A map showing contours and various strata of soils and underlying rocks composing the surface of the mapped area.
GORE (USGS) – 1) An irregularly shaped tract of land, generally triangular, left between two adjoining surveyed tracts, because of inaccuracies in the boundary surveys or as a remnant of a systematic survey.
2) A lune shaped map used in making a globe.
3) A fillet of paved surface between two merging highway lanes. See HIATUS.
GORGE – A valley which is more than usually deep and narrow, with steep walls; there is no sharp distinction between a gorge and a canyon, though the latter is generally of much greater size. The sides of a small gorge are sometimes nearly vertical.
GRAD – A European angular unit of measure equal to 1/400th of a full circle. Also spelled GRADE
GRAIN – 1) One of the discrete silver particles resulting from the development of an exposed light-sensitive material.
2) The fibers of a paper, such as that used for photographic prints.
3) The predominant direction in which fibers run.
GRAPHIC RECTIFICATION – A technique for the determination of photograph rectification by graphical means.
GRAPHIC SCALE – See BAR SCALE.
GRATICULE – 1) A network of lines.
2) The network of parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude plotted on a map, or chart according to a projection.
GRAVER – A scribing instrument for cutting through the plastic coating without disturbing the base material.
See BUILDING GRAVER, COMBINATION GRAVER, DOT GRAVER, PEN-TYPE GRAVER, RIGID GRAVER, and SWIVEL GRAVER.
GREAT CIRCLE – The line of intersection of the surface of a sphere with any plane which passes through the center of the sphere.
GREENWICH MERIDIAN – The meridian passing through the original site of the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England; uses as zero degrees longitude.
![]() Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Phone
GRID – A network composed of two sets of lines, each set drawn according to a definite pattern and intersecting the other in a specific geometric arrangement. The most common form of grid consists of uniformly spaced parallel lines intersecting at right angles.
• The term is frequently used to designate a plane-rectangular coordinate system superimposed on a map projection, in which case it generally carries the name of the projection; that is, Lambert grid, transverse Mercator grid, Universal transverse Mercator grid.
GRID AZIMUTH – Azimuth referred to the Y (or N) axis of a grid system.
GRID DISTANCE – See GRID LENGTH.
GRID LENGTH – The distance between two points obtained by inverse computation from grid coordinates of the points. It differs from the geodetic length by the amount of small correction based on the scale factor for the line.
GRID METHOD – A method of plotting detail from oblique photographs by superimposing a perspective of a grid on a photograph, thereby facilitating the transfer of detail from the photograph to a base.
GRID NORTH – The direction of the earth’s polar axis as plotted ( or computed) on a map projection.
GRID PLATE – A glass plate on which a grid is accurately ruled, used principally for the calibration of photogrammetric instruments. See RESEAU.
GRID TICK – A small mark placed at the edge of a map or drawing to indicate a measurement.
<span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: 18px;”><span style=”color: #004fbd;”><img class=”alignleft wp-image-9816″ src=”https://haller-blanchard.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/the-safe-companies-contact-us.gif” alt=”” width=”38″ height=”38″ />Please feel free to</span> <a href=”https://haller-blanchard.com/contact-land-survey-company//”>contact us</a> <span style=”color: #004fbd;”>about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. </span></span><span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; font-size: 18px;”><span style=”color: #004fbd;”>We are here now and ready to answer.</span>
</span>
GROUND CONTROL POINT – Any point that has a known location on the earth’s surface which can be identified in ERTS imagery. See CONTROL, PHOTO.
GROUND DISTANCE – A measured distance not yet reduced to sea level (geodetic) distance.
GROUND RESOLUTION – The minimum distance between two objects on the ground (or size of object on the ground) that can be detected.
GROUND SPEED – The velocity of an aircraft along a track with relation to the ground; the resultant of the heading and airspeed of an aircraft and the direction and velocity of the wind.
GROUND SURVEY – A survey made by measurement on the surface of the earth as distinguished from aerial survey.
GROUND SWING – An error condition in microwave distance measurement caused by reflected waves from water, pavement or other smooth surface. The reflected wave combines with the direct wave causing error which can be eliminated by frequency changes.
GROUND TRUTH – Term coined for information obtained on surface or subsurface features to aid in interpretation of remotely sensed data. A vague, misleading term suggesting that the truth may be found on the ground. Ground data and ground information are preferred terms.
GULCH – A small ravine; a small, shallow canyon with inclined slopes and steep sides.
GULF – A portion of the sea partially enclosed by a more or less extensive sweep of the coast. The distinction between gulf and bay is not always clearly marked, but in general a bay is wider in proportion to its amount of recession than a gulf; the latter term is applied to long landlocked portions of sea opening through a strait, which are never called bays.
GUYOT – See TABLEMOUNT.
GYROCOMPASS – A north seeking device consisting of a gimballed rotating wheel which alines itself to the earth’s rotation. Some aircraft magnetic compasses are gyroscopically stabilized and are also called gyrocompasses.
GYRO THEODOLITE – A theodolite with a gyrocompass attached.
![]() Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Please feel free to contact us about Land Survey Terms or any other questions. We are here now and ready to answer.
Phone Email us
Here is a good source for becoming a Surveyor or learning about the industry to make certain it’s the right path for your future